Last week I gave a talk at QEC Zurich, for which I had decided to speak about the potential of quantum computers built from d-level quantum systems. When preparing for the talk I discovered that not all conventional computers have used binary logic. In 1958, the first Setun computer was built at Moscow State University using ternary, or 3 state, logic. I was fascinated by this curiosity of computing, and so decided to kick off my talk with a brief mention of it. Here I’ll say a bit more about it, but really I want to invite any knowledgeable readers to tell me more about Setun! I’ve found some sources in English, but the vast majority of the literature is in Russian.

“Снимок Сетунь“. Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons.
Above is Setun’s exterior. Under the hood, it represented numbers in balanced ternary logic. Each possible value is best labelled as 0,1 or -1. Given a string of such numbers
 ,
,
they would represent a number
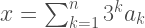 .
.
For example, the numbers from -5 to 5 are represented as
 .
.
Unlike in binary, negative numbers are naturally captured by this system without an ad hoc prefix for the sign. Many basic arithmetical operations are particularly simple. Rounding of a number to leading significant figures can be achieved by just truncating a sequence, whereas binary rounding potentially depends on the whole sequence of bits. In The Art of Computing, Donald Knuth gives a fantastic survey of different number systems, and was so enamored with balanced ternary that he said it is “perhaps the prettiest number system”.
The development of Setun was lead by Sergei Sobolev and Nikolay Brusentsov. Sobolev was a mathematician of considerable renown and influence within the Soveit union who was in the 1950s the head of computational mathematics in Moscow State University. Brusentsov was a younger engineer keen to get his teeth into modern computing, and recalling his first meeting with Sobolev said,
When I first came to Sergei Sobolev’s office, it seemed as if I was enveloped in sunlight – his face looked that kind and open. We hit it off immediately and I will be forever grateful to providence for leading me to this remarkable man, a bright mathematician and knowledgeable scientist, one of the first people who understood the significance of computers.
Together they conceived built a research team and conceived the initial design. Though Sobolev was pivotal in getting the project of the ground, Brusentsov stayed committed to Setun as Sobolev’s attention became diverted. Brunsentov recalled,
Sobolev was the heart and soul of this project. Unfortunately, his participation in our creative work ended in the early 1960s when he moved to Novosibirsk. All of his later involvement revolved around perpetual fighting with bureaucrats for the right to do the work we believed in.
Whereas, it seems Setun really became Brusentsov’s life long passion. Later in life he continued to write papers on Setun and ternary computing, until he passed away just several weeks ago.

Nikolay Brusentsov
7 February 1925 – 4 December 2014
The decision to work in ternary came earlier, and it is claimed the elegance of the number system allowed them to achieve the equivalent computing power with fewer components. At the time, transistors were not yet available and vacuum tubes were too large for a compact computer. Therefore, the decision was made to build it using magnetic cores and diodes. The first Setun was a success and they went on to built 50 such machines. However, it was always a university project, not fully endorsed by the Soviet government, and viewed suspiciously by factory management. Despite requests from abroad for Setuns to be exported, the orders were not met. Against these obstacles the Setun fizzled out, and Brusentsov’s group was moved to offices in a hostel! At least, this is the picture painted by the few sources I’ve found and read. The story is of a ingenious computing architecture that was simply the Betamax of its time. The accuracy of this narrative is hard to judge. I suppose the interesting question is how a modern ternary computer would compete or even excel against its binary contemporaries. Or even, how a quantum computer would fare by going beyond the conventional qubit paradigm.
sources:
Malinovsky, Pioneers of Soviet Computing
Russian Virtual Computer Musuem
Donald Knuth, The Art of Computing








